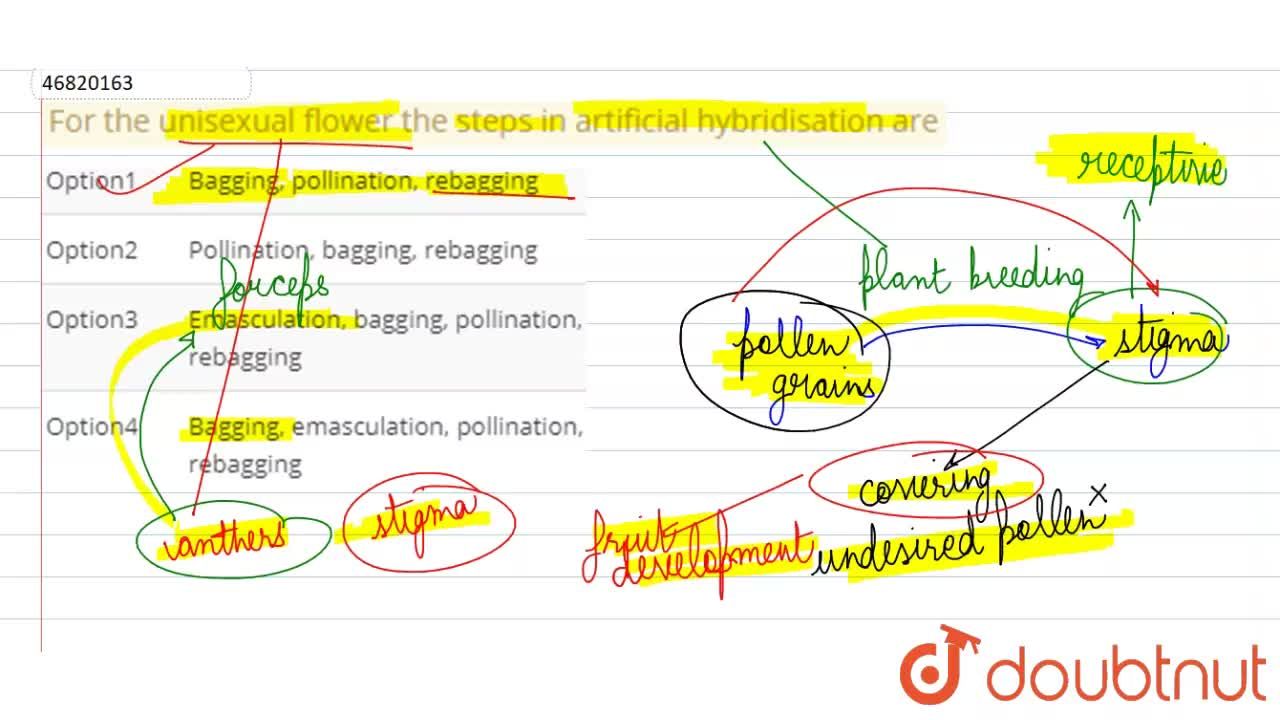
Explain the Different Steps Involved in Artificial Hybridisation
This process is called bagging. Explain the steps involved in MOET.
It should be tested for their.

. Hybrid seed production is dependent upon the control of pollination. Ii Removal of cell wall of the fusing cell with the help of the enzymes like pectinase and cellulase. 1 sp Hybridisation.
The following points highlight the five main steps of hybridization technique. The following are the types of hybridisation. Then mature and viable pollen grains are collected from the male parent the bag is opened and the pollen grains are dusted on the stigma.
Find a blooming female flower with its petals pushed back. B Mature angiosperm embryosac at maturity though 8 nucleated is 7 celled. Selection and Preparation of Parents.
Ii Artificial selection of plants with desirable traits. Steps involved in MOET. In crop improvement programmes intervarietal hybridization is the most commonly used.
There are three basic steps involved in hybrid cultivar development. Separate but compatible signal amplification systems enable the multiplex assay up to two targets per assay. The emasculated flower is immediately enclosed in a bag to prevent pollination by unwanted pollen.
Briefly write the various steps involved in female gametophyte development. The parents involved in hybridization belong to the same species. Emasculation and bagging are the two important steps carried during artificial hybridisation to obtain superior varieties of desired plants.
Explain giving reasons in which types of flowers and at what stages are the two processes carried out. Try not to touch the stamens to avoid the pollen transfer to your fingers. A cow is administered with FSH hormones it induce follicular maturation and super ovulation.
The bag is replaced immediately. 1 development of inbred parental lines 2 crossing of unrelated inbred parent lines to produce the F1 generation and 3 producing seeds for distribution. These enzymes digest the cell wall to expose the naked protoplast.
Genetic Algorithms - Introduction. They produce 6-8 egg instead of one egg per cycle. Male and female plants of the desired characters are selected.
Explain the different steps. Click hereto get an answer to your question Three Mark Questions Explain the process of artificial hybridisation to get improved crop variety in i plants bearing bisexual flowersii Female parent producing unisexual flowers. The two steps include.
Inbreeds are grown under normal conditions and are emasculated. It is the third step in hybridization. Removal of anthers from bisexual flowers of female parent plant This is done before anthers mature Prevents.
I Single cells isolated from the selected plants. The main steps involved in the genomic in situ hybridization are a direct or indirect labeling of probe b blocking DNA fragmentation c preparation of slide d denaturation of probe and blocking DNA in a hybridization mixture e addition of the probe and the blocking DNA with the hybridization mixture f chromosome DNA denaturation g hybridization of blocking DNA. Arrange the steps in correct order explain them and name the process of crop imdorvement programme with the given steps.
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology 2. Steps involved in hybridization are as follows. Cow is mated with elite bull or artificially inseminated.
The steps involved in somatic hybridization are. In such hybridisation one s- and one p-orbital are mixed to form two sp hybrid orbitals having a linear structure with bond angle 180 degrees. Ii Selfing of parents or artificial self-pollination.
It is also known as intraspecific hybridization. Genetic Algorithm GA is a search-based optimization technique based on the principles of Genetics and Natural SelectionIt is frequently used to find optimal or near-optimal solutions to difficult problems which otherwise would take a. Hybridization involves two steps.
It is a process of removal of anthers to prevent self pollination before anthesis period of opening of. The above two process are coming under Artificial Hybridisation. Touch the stamens of the male flower to the stigma of the female flower and roll over it gently.
After checking all the necessary conditions hybridization steps can be started by first adding a target-specific probe composed of 20 oligonucleotide pairs hybridizes to the target RNAs. Artificial hybridization is achieved using the following techniques. Take a male flower and remove its petals.
Emasculation Removal of anthers from bisexual flowers of female parent plant This is done before anthers mature Prevents. I crossing or hybridisation of pure lines. It is essential for inducing homozygosity for eliminating the undesirable characters and obtaining inbreeds.
Selection and Preparation of Parents 2. Hybridization Technique Step 1. If there is no lone pair of electrons then the geometry of orbitals and molecule is different.
They may be two strains varieties or races of the same species. At first plant cell wall is removed by using cellulose and pectinase enzyme after this other components of cell can be removed by protease lipase carbohydrates and RNAase.

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Explain the Different Steps Involved in Artificial Hybridisation"
Posting Komentar